The Ultimate Guide to Ransomware: What You Need to Know
Last Updated: December 17th, 2024 8 min read Servers Australia

Ransomware has emerged as one of the most dangerous and disruptive forms of cyberattacks, capable of crippling businesses, governments, and individuals alike. For small to medium-sized businesses in particular, ransomware can feel overwhelming and even impossible to prevent, but the good news is that understanding the basics and implementing key security measures can make all the difference.
This guide will take you through every critical aspect of ransomware, from how it works to actionable strategies you can use to protect your business in a disaster recovery environment. Written in clear, straightforward terms, this is the ultimate resource to help you prepare for and defend against ransomware. 5 Tips to Keep Your Business Safe from Ransomware Attacks.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malicious software designed to block access to your data or systems until you pay a ransom. Typically the attackers encrypt your files making them unreadable (CryptoLocked) and promise to provide the decryption key once payment is made.
At its core, ransomware exploits a business’s reliance on data. For many companies, access to files, client information, and essential systems is critical for day-to-day operations. When ransomware strikes, it can bring everything to a halt, leading to lost productivity, financial costs, and sometimes irreparable damage to your business’s reputation.
Imagine this...You open your computer one morning to find that all your files, including critical business documents, photos, and customer records, are locked. A message appears on your screen:
“Your files have been encrypted. Pay $10,000 in Bitcoin within 48 hours to recover them. After this deadline, your files will be permanently deleted.”
The attackers often use scare tactics, such as countdown timers, to pressure victims into paying quickly. Many victims, feeling helpless, opt to pay the ransom, hoping to regain access.
However, paying the ransom is not always the solution. Cybersecurity experts warn that paying does not guarantee the decryption key will work or that the attackers won’t target you again. In fact, paying ransoms may encourage cybercriminals to launch more attacks.
Why is Ransomware a Growing Threat?
Ransomware has become increasingly common for several reasons:
Profitability
Cybercriminals can make substantial amounts of money through ransom payments. With cryptocurrency like Bitcoin providing anonymity, attackers can operate without leaving a trail.
Ease of Attack
With Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS), even attackers with limited technical skills can rent ransomware tools online.
Targeting Small Businesses
Smaller organisations are often seen as easy targets because they lack advanced cybersecurity defences.
The Colonial Pipeline Attack
In 2021, the Colonial Pipeline, a major fuel supplier in the United States, was hit by a ransomware attack that disrupted fuel supplies across the country. The attackers gained access to the network through a single compromised password. As a result, Colonial Pipeline paid a ransom of $4.4 million to restore operations. This incident highlights how even one vulnerability can lead to massive consequences.
For businesses of all sizes, ransomware is a wake-up call. It underscores the importance of strong security measures and proactive planning.
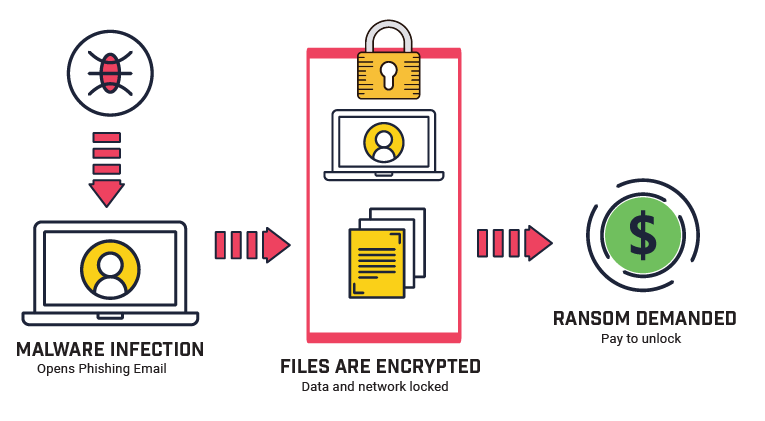
How Ransomware Works
Understanding how ransomware works is the first step in stopping it. While there are different types of ransomware, most attacks follow a similar pattern.
Delivery
How Ransomware Enters Your System
Ransomware typically enters systems through phishing emails, malicious links, or unsecured software. Phishing emails are particularly dangerous because they trick users into taking actions that allow ransomware to install itself.
You receive an email claiming to be from a trusted supplier, with an attached invoice.
The attachment looks harmless, but clicking on it downloads ransomware onto your device.
Once inside, the ransomware can spread rapidly across your network. Other methods of delivery include:
Outdated Software: Attackers exploit known vulnerabilities in software that hasn’t been updated.
Malicious Websites: Visiting compromised websites can silently install ransomware.
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Attacks: Weak passwords on remote access tools allow attackers to gain entry.
Encryption
Locking Your Files
After ransomware infiltrates your system, it begins encrypting your files. Encryption scrambles data so it can’t be read without a decryption key, which the attackers control. The process is usually quick, targeting essential files like documents, spreadsheets, and databases.
During this phase, ransomware may also delete or corrupt any backups it can find, making recovery even more difficult.
Ransom Demand
Once encryption is complete, the attackers display a ransom note with instructions for payment. These notes often include:
The ransom amount (typically demanded in cryptocurrency).
A deadline for payment.
Threats of data deletion or public release if payment isn’t made.
Attackers may also provide “proof” by decrypting a small file to demonstrate that they have the key.
The Impact of Ransomware
The consequences of a ransomware attack can be severe, affecting every aspect of a business and it's servers.
Operational Disruption
Ransomware can bring business operations to a complete standstill. Without access to essential files, even basic tasks like processing orders or sending emails become impossible. For businesses that rely heavily on data, such as legal firms, healthcare providers, and financial institutions, this disruption can be catastrophic.
Financial Loss
The financial impact of ransomware extends far beyond the ransom payment. Businesses must account for:
Downtime: Lost productivity while systems are offline.
Recovery Costs: IT support, security audits, and system restorations.
Potential Fines: Regulatory penalties if customer data is compromised.
For small businesses operating on tight budgets, these costs can be crippling.
Reputational Damage
Beyond financial loss, a ransomware attack can harm your reputation. Customers may lose trust in your ability to keep their data secure, leading to lost business. For example, if a medical clinic experiences a ransomware attack and patient records are compromised, patients may seek care elsewhere.
A Wake-Up Call for a Local Business
A retail store was hit by ransomware after an employee clicked on a phishing email disguised as a shipping notice. The attack encrypted their sales database, inventory records, and customer details. Without backups, the business had no choice but to pay the ransom.
Although they regained access, the ordeal cost them valuable time and money. The incident served as a wake-up call, prompting them to implement better security practices, such as employee training and automated backups.
How to Prevent a Ransomware Attack
Ransomware prevention involves a combination of technical solutions, employee awareness, and proactive planning. Here are the most effective strategies.
Backup Your Data Regularly
Backups are your best defence against ransomware. If your files are encrypted, having recent backups allows you to restore data without paying the ransom. Use a combination of cloud backups and offline backups to ensure redundancy. Store offline backups on devices disconnected from your network to prevent ransomware from tampering with them.
If your files are encrypted, having recent backups allows you to restore data without paying the ransom. Use a combination of cloud backups and offline backups to ensure redundancy.
Train Your Employees
Employees are often the weakest link in cybersecurity. Train your team to recognise phishing emails, avoid suspicious links, and verify unexpected attachments. Regular cybersecurity training reduces the risk of human error.
Update Software and Systems
Keep your operating systems, software, and antivirus programs up to date. Regular updates close security vulnerabilities that attackers exploit. Enable automatic updates where possible to ensure your systems remain protected.
Use Endpoint Security Solutions
Endpoint security protects devices like laptops and desktops from ransomware. Modern security solutions include antivirus software, firewalls, and real-time monitoring to detect threats before they can cause damage.
Adopt Zero Trust Architecture
A Zero Trust approach assumes that no user or device can be trusted by default. Access to systems and data is restricted to only those who need it. This limits the spread of ransomware if an attacker gains entry.
5 steps to respond to a Ransomware Attack
If you find yourself under attack, here’s what you need to do:
Isolate the Infection:
Immediately disconnect affected devices from the network, including Wi-Fi, wired connections, and external drives, to prevent the ransomware from spreading further.Shut Down Compromised Systems:
Turn off all infected machines and servers to contain the malware. Ensure no new devices connect to the network until the situation is assessed.Contact IT Support or Cybersecurity Experts:
Engage IT professionals, a managed security provider, or a ransomware recovery specialist to assess the extent of the damage, identify the type of ransomware, and determine the best course of action.Restore Systems From Clean Backups:
Use verified and secure backups to restore your systems. Ensure backups are free of ransomware before proceeding. Avoid paying the ransom, as it doesn’t guarantee file recovery and may encourage further attacks.Report the Incident and Strengthen Defenses:
Notify law enforcement or relevant authorities about the attack. Follow legal obligations for reporting data breaches. Post-recovery, conduct a full cybersecurity audit, implement stronger defences, and educate staff to prevent future incidents.
The Future of Ransomware
Ransomware is evolving, with attackers adopting new tactics like double extortion, where they threaten to leak stolen data. The rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) has made it easier for cybercriminals to launch attacks, while emerging vulnerabilities in IoT devices and remote work systems present new risks.
Taking Action Against Ransomware
Ransomware may be a growing threat, but it is not unstoppable. By understanding how it works, implementing strong security practices, and preparing for potential attacks, you can protect your business and data. Don’t wait until ransomware strikes to take action, start building your defences today.



